Key Takeaways
- Brain development continues until age 32, redefining adolescence
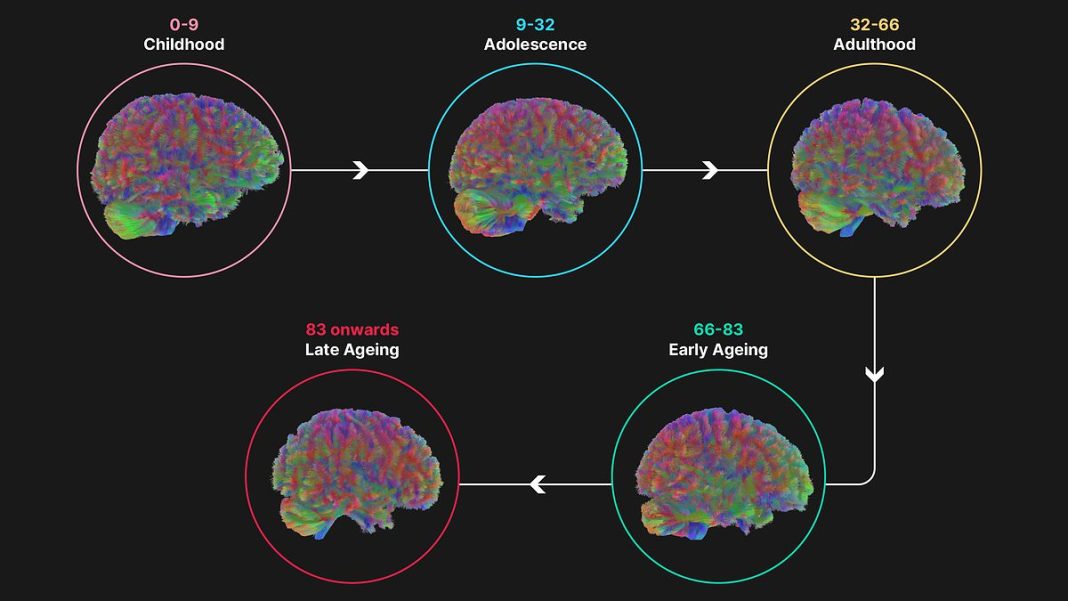
- Five distinct stages shape cognitive abilities across lifespan
- Early 30s mark the “strongest topological turning point” in brain wiring
Groundbreaking research reveals the human brain progresses through five distinct developmental stages, with adolescence extending well into our early 30s. A comprehensive University of Cambridge study analyzing 3,802 brain scans from ages 0 to 90 identifies four pivotal turning points that define our neurological journey from childhood to late ageing.
The Five Brain Development Stages
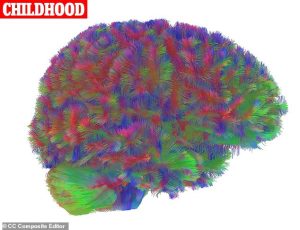
Childhood (0-9 years)
During this foundational period, the brain undergoes massive reconfiguration through “network consolidation.” Excess neural connections are pruned while only the most active synapses survive. Grey and white matter expand rapidly, and the brain’s characteristic ridges stabilize.
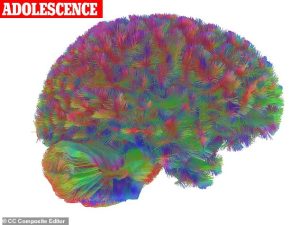
Adolescence (9-32 years)
Contrary to conventional understanding, adolescence spans nearly three decades. “The brain goes through a natural transition around puberty begins, which extends until the early 30s,” explains lead researcher Dr Alexa Mousley. This period features increasingly refined and efficient neural connections, enhancing cognitive performance.
“Efficiency in the brain is similar to how you’d think of an efficient path between two places – a short, direct route. When short paths that allow for communication between brain regions form or strengthen, the brain becomes more efficient.”
The early 30s represent the “strongest topological turning point” of our lives. However, this extended adolescence also correlates with increased mental health disorder prevalence.
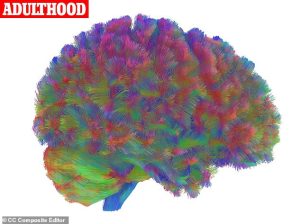
Adulthood (32-66 years)
Brain architecture stabilizes during this longest phase, with intelligence and personality reaching a plateau. Increased segregation emerges as brain regions become more compartmentalized.
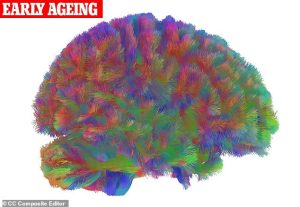
Early Ageing (66-83 years)
This mild transition period shows gradual connectivity reduction and white matter degradation. Dr Mousley notes this age brings increased risk for brain-affecting conditions like hypertension.
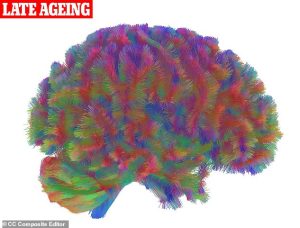
Late Ageing (83+ years)
Whole-brain connectivity declines dramatically, forcing increased reliance on specific regions. Dr Mousley illustrates: “Imagine you normally take one bus to work. If that route shuts down, you might need two buses. Suddenly, the transfer stop becomes much more important.”
Research Methodology and Implications
The Nature Communications study utilized MRI diffusion scans tracking water molecule movement to map neural connections. Professor Duncan Astle emphasizes: “Many neurodevelopmental, mental health and neurological conditions are linked to how the brain is wired. Differences in brain wiring predict difficulties with attention, language, memory, and behaviors.”
This research provides new understanding of brain development timelines and their connection to across the lifespan.