Key Takeaways
- First-ever direct detection of a coronal mass ejection (CME) from a star beyond our Solar System
- The violent eruption occurred on a red dwarf star 130 light-years away
- Event was powerful enough to strip away planetary atmospheres, threatening habitability
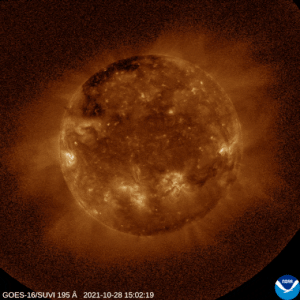
In a historic astronomical breakthrough, scientists have captured definitive evidence of a sun-like explosion on a distant star 130 light-years from Earth. This marks the first direct observation of a coronal mass ejection occurring outside our Solar System.
The discovery was made using the European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton space observatory and the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) radio telescope. It confirms that stars beyond our Sun can unleash similar violent eruptions capable of stripping away entire planetary atmospheres.
Decades-Long Search Ends
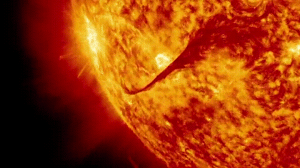
Coronal mass ejections are massive expulsions of plasma and magnetic fields from a star’s surface. While common on our Sun where they drive space weather and create auroras, astronomers had never directly witnessed one erupting from another star until this detection.
“Astronomers have wanted to spot a CME on another star for decades,” said Joe Callingham, lead author of the study published in Nature. “Previous hints existed, but this is the first time we’ve definitively seen material escape into space.”
How Scientists Detected the Stellar Eruption
The research team identified an intense, short-lived radio signal generated as the CME raced through the star’s magnetic atmosphere. The emission was far too powerful to exist within a stellar magnetic bubble, confirming that material had truly broken free into space.
The source star was identified as a red dwarf – a small, cool star type known for high magnetic activity. The eruption reached astonishing speeds of approximately 2,400 kilometers per second, exceeding even the most powerful solar CMEs observed on our Sun.
Implications for Alien Life
This discovery carries significant consequences for the search for extraterrestrial life. Red dwarfs constitute the majority of stars in our galaxy and frequently host Earth-sized exoplanets within their habitable zones.
However, if these stars regularly produce massive CMEs like the one detected, they could strip away the atmospheres of otherwise potentially habitable worlds, rendering them barren.
LOFAR’s high sensitivity enabled the radio detection while XMM-Newton provided crucial X-ray data about the star’s temperature and activity levels.
“Neither telescope alone would have been enough — we needed both to prove it was really a CME,” said co-author David Konijn of ASTRON.
“This work opens a new frontier for studying stellar space weather,” said ESA researcher Henrik Eklund. “The next step is understanding how such eruptions affect the long-term survival of planetary atmospheres, and by extension, the potential for life itself.”
The findings open new avenues for understanding and its impact on throughout our galaxy.