Gaganyaan Mission Timeline Under Scrutiny
ISRO’s ambitious Gaganyaan mission faces potential delays as speculation grows about the timeline for its first uncrewed test flight. While officials maintain the December 2025 target, the space agency chairman’s recent silence on the schedule has raised questions.
Key Updates on Gaganyaan Mission Status
- ISRO chairman Dr. V. Narayanan avoided confirming the December 2025 timeline for G1 mission
- Three uncrewed flights planned before crewed mission
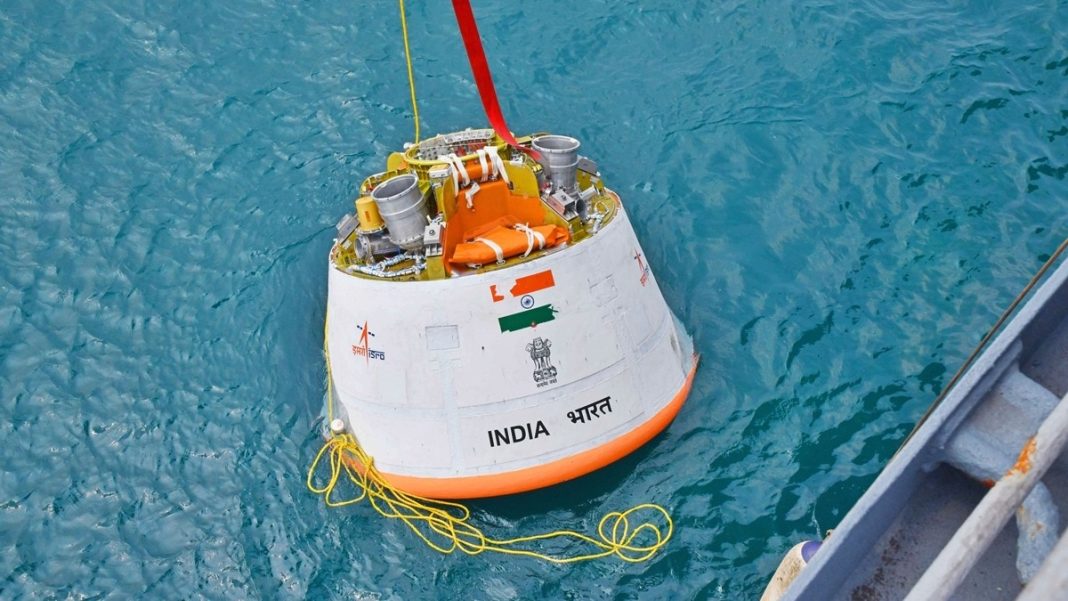
- All hardware has arrived at Sriharikota with integration underway “at war speed”
- First uncrewed mission to feature Vyomitra humanoid robot
Mission Details and Current Progress
The inaugural Gaganyaan G1 mission will carry Vyomitra, an Indian-developed humanoid robot, to test crew module performance, life-support systems, and safety under actual spaceflight conditions. Senior ISRO sources confirm that hardware integration is progressing rapidly at Sriharikota.
“Our Gaganyaan programme is progressing well. It is in advanced stages. All hardware have arrived at Sriharikota and integration (of the hardware) is happening. We have planned three uncrewed mission. The first uncrewed mission, ‘G1 Mission’, is going to be achieved before the end of the current financial year,”
Broader Timeline and Concerns
Narayanan outlined ISRO’s plan to launch seven missions, including all three uncrewed Gaganyaan flights, before March 2026. However, experts warn that any delay could compress all test flights into 2026, increasing pressure on the eventual crewed launch timeline.
The Gaganyaan project represents India’s most significant space technological leap since its 2018 announcement, having overcome pandemic-related delays and the inherent complexity of human spaceflight systems. Success would place India among the elite group of nations – United States, Russia, and China – with independent human spaceflight capability.
All attention now focuses on ISRO’s next official update as the agency works to maintain schedule for India’s historic entry into human space exploration.